Product Description
SS Rigid stainless metal grooved coupling / pipe clamp / quick coupling
Rigid coupling SS acid resistant stainless metal coupling is designed to be used with SCH5S-SCH40S stainless metal pipes.
Operating strain: 350PSI, 600Psi,1200PSI
2.5Mpa,4.2Mpa, 8.3Mpa
Resources
Housing: Type CF8M (316) stainless steel ASTM A351, A743 or A744 Gr. CF-8M
Bolts & nuts: Stainless metal ASTM A193 B-8
Gasket
Normal gasket: Class “E” EPDM: Advised to be used with chilly and hot water inside the temperature range -34 °C – +110 °C. Can also be utilized with diluted acids, oil-free of charge air and several different substances. Not recommended to be used with oils, mineral oils, solvents or fragrant hydrocarbons.
Option gasket: Class “T” Nitrile: (Color code: Orange). Temperature selection: -29 °C – + eighty two °C. Advisable to be utilised with oil merchandise, oil made up of air, vegetable and mineral oils within the offered temperature variety. Also with water below +sixty six °C. Not to be utilised with Very hot Drinking water more than +sixty six °C or Scorching DRY AIR above +60 °C.
Alternate options:
Class “O” – Fluoroelastomer
Course “L” – Silicone
Dimensions
| DN | D (mm) | Length amongst pipe finishes (mm) | X (mm) | Y (mm) | Z (mm) | Bolt measurement (mm) | Fat (kg) |
| twenty five | 33.four | -2.2 | 54. | 100 | 44 | M10x50 | .5 |
| 32 | 42.2 | -2.2 | sixty two. | 108 | 44 | M10x50 | .six |
| 40 | forty eight.3 | -2.2 | sixty eight. | 114 | 44 | M10x50 | .6 |
| 50 | 60.3 | -2.2 | 81. | 128 | forty five | M10x50 | .seven |
| sixty five | seventy six.one | -2.2 | ninety eight. | one hundred forty four | forty six | M10x50 | .nine |
| eighty | 88.9 | -2.6 | 111. | 161 | forty seven | M10x50 | 1. |
| one hundred | 114.three | -2.6 | 140. | 189 | 48 | M10x60 | one.4 |
| a hundred twenty five | 139.seven | -2.6 | 167. | 227 | forty nine | M12x70 | 2. |
| one hundred fifty | 168.3 | -2.6 | 197. | 256 | 49 | M12x70 | 2.3 |
| two hundred | 219.1 | -4.9 | 254. | 322 | 59 | M16x90 | four.2 |
| *250 | 273. | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| *300 | 323.9 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
Technological information
| DN | D (mm) | Max doing work strain Sch 40S (Bar) |
Max tensile energy Sch 40S2 (kN) |
Max working pressure Sch 10S (Bar) |
Max tensile strength Sch 10S2 (kN) |
Max working stress Sch 5S (Bar) |
Max tensile strength Sch 5S2 (kN) |
| twenty five | 33.four | twenty five | four.6 | twenty five | 3.seven | sixteen | 2.5 |
| 32 | 42.two | 25 | 7.three | twenty five | five.nine | sixteen | 3.nine |
| forty | forty eight.3 | 25 | 9.5 | 25 | seven.7 | sixteen | 5.one |
| fifty | 60.three | twenty five | 14.nine | 25 | twelve. | 16 | 8. |
| 65 | 76.one | 25 | 19.1 | twenty five | 15.9 | sixteen | 10.nine |
| 80 | 88.nine | 25 | 26.one | 25 | 21.seven | 16 | 14.9 |
| 100 | 114.three | twenty five | 35.nine | 25 | 35.9 | 16 | 24.six |
| a hundred twenty five | 139.7 | 16 | 42.9 | sixteen | 42.nine | ten | 32.2 |
| 150 | 168.three | sixteen | 62.three | 16 | sixty two.three | 10 | 46.7 |
| 200 | 219.1 | 16 | 79.two | sixteen | seventy nine.2 | 10 | fifty two.8 |
| *250 | 273. | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| *three hundred | 323.9 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
* Not a stock product, verify supply time and specs.
** Only use resources and gear supposed for stainless metal when grooving stainless steel pipes during installation.
Our organization is engaged in the creation and trade of all types of Stainless Metal Grooved Pipe Coupling completed and unfinished goods. Stainless Metal Grooved Pipe Coupling is our main manufacturing and offer well. We have recognized business interactions with clients in the Korea, Japan, Singapore, Iran, Dubai, Yemen, Chile, Brazil, France, Uk, Italy, Canada and much more than twenty international locations and regions for Stainless Steel Grooved Pipe Coupling Annual product sales profits is USD 50 billion. The particulars of payment strategy, shipping time and minimium quantity and so on for Stainless Steel Grooved Pipe Coupling can be negotiated in accordance to the get.
| Connection: | Female |
|---|---|
| Structure: | Metal Bellows |
| Flexible or Rigid: | Rigid |
| Material: | Stainless Steel |
| Standard: | Standard |
| Packaging Detail: | Product Packaged in Cartons on Wood Pallet or Case |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| DN | D (mm) | Distance between pipe ends (mm) | X (mm) | Y (mm) | Z (mm) | Bolt size (mm) | Weight (kg) |
| 25 | 33.4 | 0-2.2 | 54.0 | 100 | 44 | M10x50 | 0.5 |
| 32 | 42.2 | 0-2.2 | 62.0 | 108 | 44 | M10x50 | 0.6 |
| 40 | 48.3 | 0-2.2 | 68.0 | 114 | 44 | M10x50 | 0.6 |
| 50 | 60.3 | 0-2.2 | 81.0 | 128 | 45 | M10x50 | 0.7 |
| 65 | 76.1 | 0-2.2 | 98.0 | 144 | 46 | M10x50 | 0.9 |
| 80 | 88.9 | 0-2.6 | 111.0 | 161 | 47 | M10x50 | 1.0 |
| 100 | 114.3 | 0-2.6 | 140.0 | 189 | 48 | M10x60 | 1.4 |
| 125 | 139.7 | 0-2.6 | 167.0 | 227 | 49 | M12x70 | 2.0 |
| 150 | 168.3 | 0-2.6 | 197.0 | 256 | 49 | M12x70 | 2.3 |
| 200 | 219.1 | 0-4.9 | 254.0 | 322 | 59 | M16x90 | 4.2 |
| *250 | 273.0 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| *300 | 323.9 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
###
| DN | D (mm) | Max working pressure Sch 40S (Bar) |
Max tensile strength Sch 40S2 (kN) |
Max working pressure Sch 10S (Bar) |
Max tensile strength Sch 10S2 (kN) |
Max working pressure Sch 5S (Bar) |
Max tensile strength Sch 5S2 (kN) |
| 25 | 33.4 | 25 | 4.6 | 25 | 3.7 | 16 | 2.5 |
| 32 | 42.2 | 25 | 7.3 | 25 | 5.9 | 16 | 3.9 |
| 40 | 48.3 | 25 | 9.5 | 25 | 7.7 | 16 | 5.1 |
| 50 | 60.3 | 25 | 14.9 | 25 | 12.0 | 16 | 8.0 |
| 65 | 76.1 | 25 | 19.1 | 25 | 15.9 | 16 | 10.9 |
| 80 | 88.9 | 25 | 26.1 | 25 | 21.7 | 16 | 14.9 |
| 100 | 114.3 | 25 | 35.9 | 25 | 35.9 | 16 | 24.6 |
| 125 | 139.7 | 16 | 42.9 | 16 | 42.9 | 10 | 32.2 |
| 150 | 168.3 | 16 | 62.3 | 16 | 62.3 | 10 | 46.7 |
| 200 | 219.1 | 16 | 79.2 | 16 | 79.2 | 10 | 52.8 |
| *250 | 273.0 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| *300 | 323.9 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Connection: | Female |
|---|---|
| Structure: | Metal Bellows |
| Flexible or Rigid: | Rigid |
| Material: | Stainless Steel |
| Standard: | Standard |
| Packaging Detail: | Product Packaged in Cartons on Wood Pallet or Case |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| DN | D (mm) | Distance between pipe ends (mm) | X (mm) | Y (mm) | Z (mm) | Bolt size (mm) | Weight (kg) |
| 25 | 33.4 | 0-2.2 | 54.0 | 100 | 44 | M10x50 | 0.5 |
| 32 | 42.2 | 0-2.2 | 62.0 | 108 | 44 | M10x50 | 0.6 |
| 40 | 48.3 | 0-2.2 | 68.0 | 114 | 44 | M10x50 | 0.6 |
| 50 | 60.3 | 0-2.2 | 81.0 | 128 | 45 | M10x50 | 0.7 |
| 65 | 76.1 | 0-2.2 | 98.0 | 144 | 46 | M10x50 | 0.9 |
| 80 | 88.9 | 0-2.6 | 111.0 | 161 | 47 | M10x50 | 1.0 |
| 100 | 114.3 | 0-2.6 | 140.0 | 189 | 48 | M10x60 | 1.4 |
| 125 | 139.7 | 0-2.6 | 167.0 | 227 | 49 | M12x70 | 2.0 |
| 150 | 168.3 | 0-2.6 | 197.0 | 256 | 49 | M12x70 | 2.3 |
| 200 | 219.1 | 0-4.9 | 254.0 | 322 | 59 | M16x90 | 4.2 |
| *250 | 273.0 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| *300 | 323.9 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
###
| DN | D (mm) | Max working pressure Sch 40S (Bar) |
Max tensile strength Sch 40S2 (kN) |
Max working pressure Sch 10S (Bar) |
Max tensile strength Sch 10S2 (kN) |
Max working pressure Sch 5S (Bar) |
Max tensile strength Sch 5S2 (kN) |
| 25 | 33.4 | 25 | 4.6 | 25 | 3.7 | 16 | 2.5 |
| 32 | 42.2 | 25 | 7.3 | 25 | 5.9 | 16 | 3.9 |
| 40 | 48.3 | 25 | 9.5 | 25 | 7.7 | 16 | 5.1 |
| 50 | 60.3 | 25 | 14.9 | 25 | 12.0 | 16 | 8.0 |
| 65 | 76.1 | 25 | 19.1 | 25 | 15.9 | 16 | 10.9 |
| 80 | 88.9 | 25 | 26.1 | 25 | 21.7 | 16 | 14.9 |
| 100 | 114.3 | 25 | 35.9 | 25 | 35.9 | 16 | 24.6 |
| 125 | 139.7 | 16 | 42.9 | 16 | 42.9 | 10 | 32.2 |
| 150 | 168.3 | 16 | 62.3 | 16 | 62.3 | 10 | 46.7 |
| 200 | 219.1 | 16 | 79.2 | 16 | 79.2 | 10 | 52.8 |
| *250 | 273.0 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| *300 | 323.9 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
What Is a Coupling?
A coupling is a mechanical device that links two shafts together and transmits power. Its purpose is to join rotating equipment while permitting a small amount of misalignment or end movement. Couplings come in a variety of different types and are used in a variety of applications. They can be used in hydraulics, pneumatics, and many other industries.
Types
Coupling is a term used to describe a relationship between different modules. When a module depends on another, it can have different types of coupling. Common coupling occurs when modules share certain overall constraints. When this type of coupling occurs, any changes to the common constraint will also affect the other modules. Common coupling has its advantages and disadvantages. It is difficult to maintain and provides less control over the modules than other types of coupling.
There are many types of coupling, including meshing tooth couplings, pin and bush couplings, and spline couplings. It is important to choose the right coupling type for your specific application to get maximum uptime and long-term reliability. Listed below are the differences between these coupling types.
Rigid couplings have no flexibility, and require good alignment of the shafts and support bearings. They are often used in applications where high torque is required, such as in push-pull machines. These couplings are also useful in applications where the shafts are firmly attached to one another.
Another type of coupling is the split muff coupling. This type is made of cast iron and has two threaded holes. The coupling halves are attached with bolts or studs.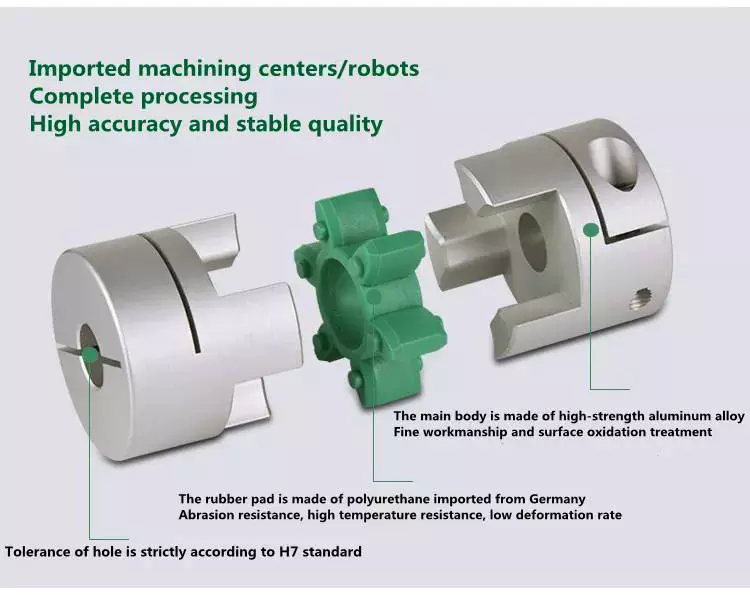
Applications
The coupling function is an incredibly versatile mathematical tool that can be used in many different scientific domains. These applications range from physics and mathematics to biology, chemistry, cardio-respiratory physiology, climate science, and electrical engineering. The coupling function can also help to predict the transition from one state to another, as well as describing the functional contributions of subsystems in the system. In some cases, it can even be used to reveal the mechanisms that underlie the functionality of interactions.
The coupling selection process begins with considering the intended use of the coupling. The application parameters must be determined, as well as the operating conditions. For example, if the coupling is required to be used for power transmission, the design engineer should consider how easily the coupling can be installed and serviced. This step is vital because improper installation can result in a more severe misalignment than is specified. Additionally, the coupling must be inspected regularly to ensure that the design parameters remain consistent and that no detrimental factors develop.
Choosing the right coupling for your application is an important process, but it need not be difficult. To find the right coupling, you must consider the type of machine and environment, as well as the torque, rpm, and inertia of the system. By answering these questions, you will be able to select the best coupling for your specific application.
Problems
A coupling is a device that connects two rotating shafts to transfer torque and rotary motion. To achieve optimal performance, a coupling must be designed for the application requirements it serves. These requirements include service, environmental, and use parameters. Otherwise, it can prematurely fail, causing inconvenience and financial loss.
In order to prevent premature failure, couplings should be properly installed and maintained. A good practice is to refer to the specifications provided by the manufacturer. Moreover, it is important to perform periodic tests to evaluate the effectiveness of the coupling. The testing of couplings should be performed by qualified personnel.

editor by czh 2023-01-16