Product Description
| Product Name | Coupling | Place of origin | China |
| Brand | 1008-5050,6050-12100 | Material | Cast Iron GG22-GG25,Steel C45 |
| QD Bushing model | H/JA/SH/SDS/SD/SK/SF/E/F/J/M/N/P/W/S,orG/H/P1/P2/P3/B/Q1/Q2/Q3/R1/R2/S1/S2/U0 /U1/U2/W1/W2/Y0 |
||
1. Engineering: machine tools, foundry equipments, conveyors, compressors, painting systems, etc.
2. Pharmaceuticals& Food Processing: pulp mill blowers, conveyor in warehouse, agitators, grain, boiler, bakery machine, labeling machine, robots, etc.
3. Agriculture Industries: cultivator, rice winnower tractor, harvester, rice planter, farm equipment, etc.
4. Texitile Mills: looms, spinning, wrappers, high-speed auto looms, processing machine, twister, carding machine, ruler calendar machine, high speed winder, etc.
5. Printing Machinery: newspaper press, rotary machine, screen printer machine, linotype machine offset printer, etc.
6. Paper Industries: chipper roll grinder, cut off saw, edgers, flotation cell and chips saws, etc.
7. Building Construction Machinery: buffers, elevator floor polisher mixing machine, vibrator, hoists, crusher, etc.
8. Office Equipments: typewriter, plotters, camera, money drive, money sorting machine, data storage equipment, etc.
9. Glass and Plastic Industries: conveyor, carton sealers, grinders, creeper paper manufacturing machine, lintec backing, etc.
10. Home Appliances: vacuum cleaner, laundry machine, icecream machine, sewing machine, kitchen equipments, etc.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
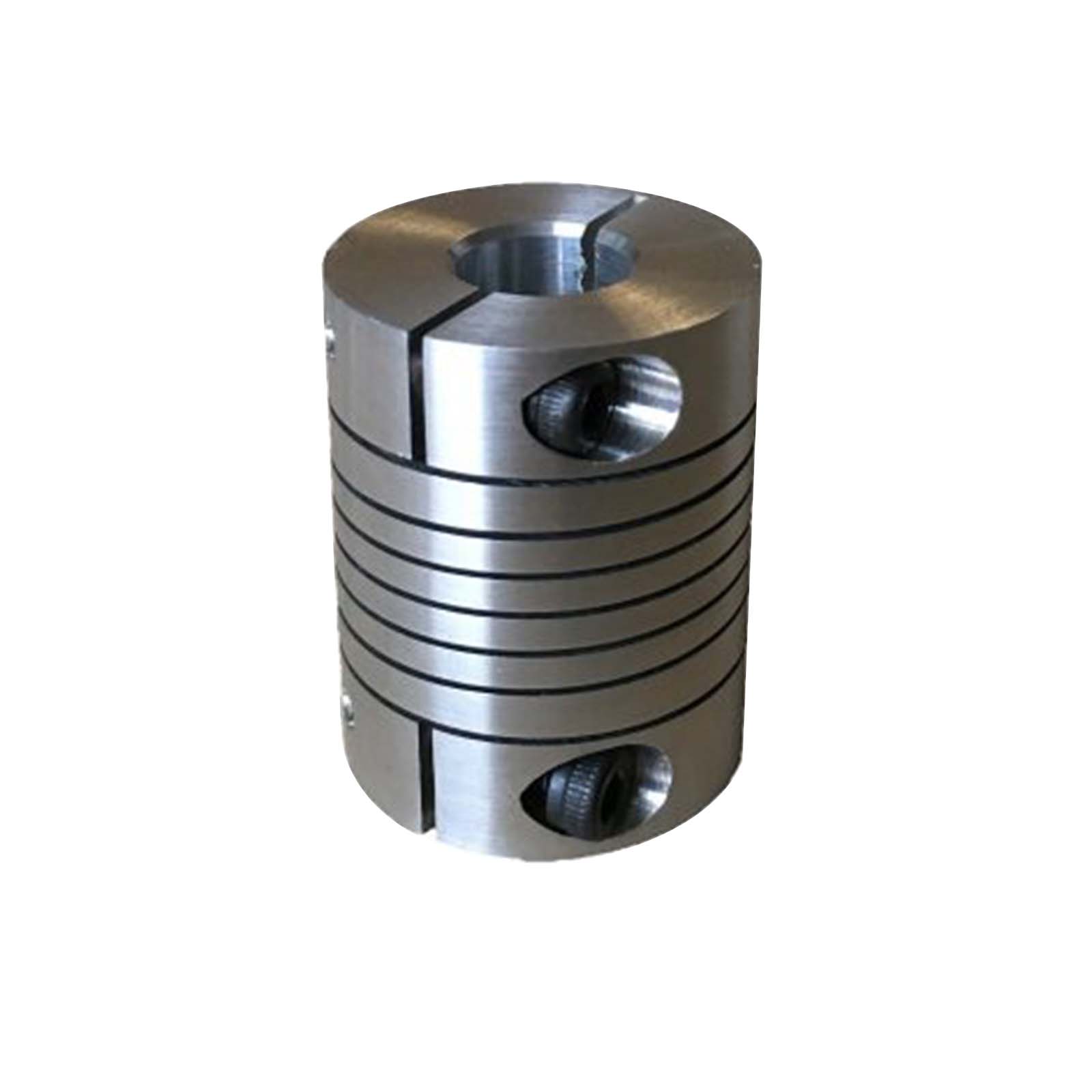

Temperature and Environmental Limits for Various Beam Coupling Materials
The temperature and environmental limits of beam coupling materials depend on their specific composition and properties. Different materials have varying degrees of resistance to temperature extremes, chemicals, humidity, and other environmental factors. Here are some common beam coupling materials and their associated temperature and environmental limits:
- 1. Stainless Steel:
Stainless steel beam couplings are known for their excellent mechanical properties and resistance to corrosion. They can typically operate within a wide temperature range, from -40°C to 300°C (-40°F to 572°F). Stainless steel is also resistant to most chemicals, making it suitable for various environments, including industrial and outdoor applications.
- 2. Aluminum:
Aluminum beam couplings offer lightweight construction and moderate mechanical properties. They have a more limited temperature range compared to stainless steel, typically operating between -20°C to 120°C (-4°F to 248°F). While aluminum has good corrosion resistance in certain environments, it is not as durable as stainless steel in harsh conditions.
- 3. Brass:
Brass beam couplings have reasonable mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. They are suitable for applications with temperatures ranging from -20°C to 100°C (-4°F to 212°F). Brass is more susceptible to corrosion in certain environments, so it is essential to consider the specific application’s conditions.
- 4. Plastic/Polymer:
Beam couplings made from plastic or polymer materials offer lightweight and cost-effective solutions. However, their temperature limits are more restricted compared to metal couplings. They typically operate between -30°C to 80°C (-22°F to 176°F). These couplings may not be suitable for high-temperature or chemically aggressive environments.
- 5. Carbon Steel:
Carbon steel beam couplings are known for their strength and mechanical properties. They generally operate between -40°C to 120°C (-40°F to 248°F). Carbon steel is vulnerable to corrosion, so it may not be ideal for applications in corrosive or humid environments without proper protection.
It’s crucial to consider the temperature and environmental conditions of your specific application when selecting a beam coupling material. Choosing a material that can withstand the intended operating conditions will ensure the longevity and reliable performance of the coupling.
Additionally, keep in mind that various beam coupling manufacturers may offer specific variations of materials with different properties and limits. Always refer to the manufacturer’s datasheets and technical documentation for precise information on the temperature and environmental limits of their beam coupling products.
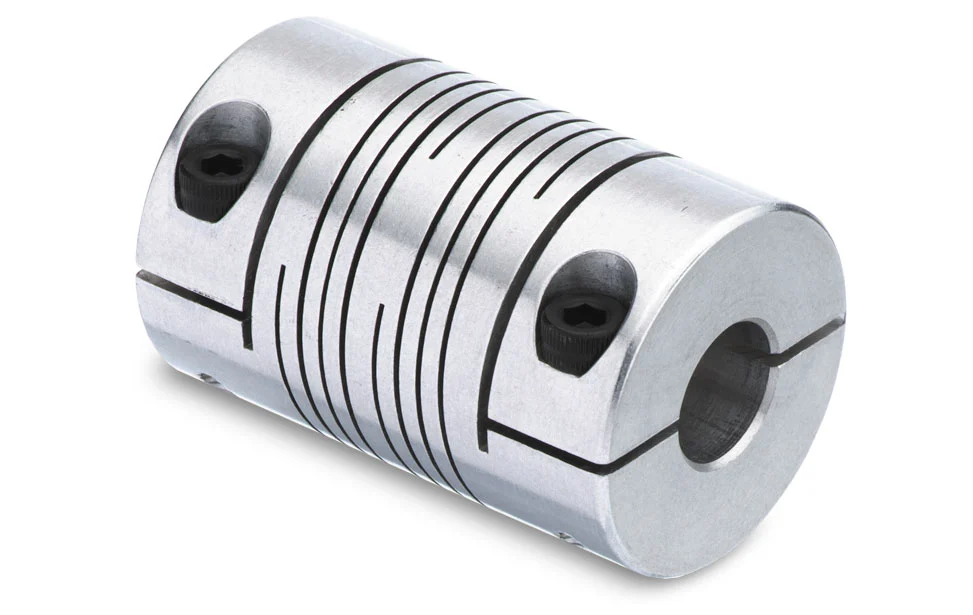

Beam Couplings Accommodating Different Shaft Diameters and Mounting Configurations
Beam couplings are highly versatile and can accommodate different shaft diameters and mounting configurations, making them suitable for a wide range of motion control applications. Their design and construction allow for flexibility in adapting to various shaft sizes and mounting setups. Here’s how beam couplings achieve this:
- Multiple Bore Sizes:
Beam couplings are available in various bore sizes to match different shaft diameters. Manufacturers offer a wide range of coupling sizes, ensuring that there is an appropriate coupling size available to fit the specific shaft diameter of your application. Some beam couplings come with set screws or clamps that securely fasten onto the shafts, accommodating shafts of different sizes within the coupling’s specified range.
- Clamp or Set Screw Mounting:
Beam couplings commonly employ clamp or set screw mounting methods to connect to the shafts. Clamp-style couplings use split hubs that can be tightened around the shaft with screws, providing a secure and concentric connection. Set screw couplings, on the other hand, utilize screws to press against the shaft, achieving a firm and non-marring grip.
- Step Bores and Adapters:
In cases where the shafts have significantly different diameters or when transitioning between metric and imperial measurements, some beam couplings offer step bores or adapter options. Step bores feature multiple bore sizes within the same coupling, allowing for flexibility in accommodating various shaft diameters. Adapters are also available to bridge the gap between different shaft sizes.
- Customization:
For unique or specialized applications, manufacturers may offer customization options for beam couplings. This could include modifying the bore sizes, lengths, or other design parameters to suit specific shaft dimensions and mounting configurations.
- Compatibility with Misalignment:
Beam couplings are designed to handle misalignment between the shafts. This characteristic provides additional flexibility during installation, as it can compensate for slight positioning errors or misalignment during assembly.
When selecting a beam coupling for your application, ensure that the chosen coupling size matches the shaft diameters within the specified range. Also, consider the mounting method that best suits your setup, whether it’s clamp-style or set screw-type. For applications with specific requirements, such as adapting between different shaft sizes, explore options with step bores or adapters or inquire about custom solutions from coupling manufacturers.
Overall, the ability of beam couplings to accommodate different shaft diameters and mounting configurations makes them a versatile and widely-used choice in motion control systems across various industries.

Beam Coupling: Function and Role in Mechanical Systems
A beam coupling, also known as a helical coupling or helical beam coupling, is a type of flexible coupling used in mechanical systems to connect two shafts while compensating for misalignment and transmitting torque. It consists of one or more helical beams (usually made of metal) that connect the shafts and allow for angular, axial, and parallel misalignment while maintaining a torsionally rigid connection. Here’s how a beam coupling functions in mechanical systems:
Structure:
A beam coupling typically has two ends, each with a helical beam. The beams are oriented at opposite angles to create a helix shape. The beams can vary in number, and some designs may include additional features like slits or keyways to enhance flexibility or improve torque capacity.
Misalignment Compensation:
When the two shafts connected by a beam coupling are misaligned, the helical beams flex, allowing the coupling to compensate for different types of misalignment. Angular misalignment occurs when the shafts are not collinear, axial misalignment when they are not on the same axis, and parallel misalignment when the shafts are not at the same height. The flexibility of the helical beams allows the coupling to accommodate these misalignments, reducing the stresses on the connected components.
Torque Transmission:
The helical beams of a beam coupling efficiently transmit torque from one shaft to the other. The beams twist and deform slightly under the applied torque but return to their original shape once the torque is removed. This torsional rigidity ensures that the coupling efficiently transfers rotational power while minimizing backlash and maintaining accurate positioning in motion control systems.
Damping and Vibration Absorption:
Beam couplings can provide some level of vibration dampening due to their inherent flexibility. The slight deformation of the beams can absorb shocks and vibrations, reducing the transmission of vibrations between the connected shafts.
Applications:
Beam couplings find applications in various mechanical systems, including robotics, CNC machines, stepper motor drives, and other motion control systems. They are especially useful in applications that require moderate misalignment compensation, high torsional rigidity, and low backlash.
Considerations:
While beam couplings offer several advantages, they do have some limitations. They may not be suitable for applications with high misalignment requirements or high torque loads, as excessive misalignment or torque can cause premature wear or failure of the coupling. Additionally, beam couplings may have limited axial stiffness, making them less suitable for applications with significant axial loads.
In summary, a beam coupling is a flexible coupling with helical beams that allows for misalignment compensation, efficient torque transmission, and some vibration dampening. Its design and flexibility make it an excellent choice for various mechanical systems, particularly those that require moderate misalignment compensation and high torsional rigidity.


editor by CX 2024-04-26