Product Description
transmission parts Flexible Universal Ship Shaft Flange Flexible Rub double standard rigid jaw beam universal shaft aluminum roller Chain Coupling
Application of Chain Coupling
Chain couplings are used to connect 2 shafts that are not perfectly aligned. They are made up of a series of interlocking links that allow the shafts to move slightly relative to each other without losing power transmission. Chain couplings are available in a variety of sizes and styles to accommodate different applications.
Here are some of the most common applications for chain couplings:
- Conveyors: Chain couplings are used to connect the drive shaft of a conveyor to the conveyor belt. This allows the conveyor to move smoothly and efficiently, even if the belt is not perfectly aligned with the shaft.
- Pumps: Chain couplings are used to connect the drive shaft of a pump to the pump impeller. This allows the pump to move fluids smoothly and efficiently, even if the impeller is not perfectly aligned with the shaft.
- Fans: Chain couplings are used to connect the drive shaft of a fan to the fan blades. This allows the fan to move air smoothly and efficiently, even if the blades are not perfectly aligned with the shaft.
- Actuators: Chain couplings are used to connect the drive shaft of an actuator to the actuator arm. This allows the actuator to move objects smoothly and precisely, even if the arm is not perfectly aligned with the shaft.
Chain couplings are a versatile and reliable way to transmit power from 1 shaft to another. They are used in a wide variety of applications, and they can help to improve the efficiency and safety of many different operations.
Here are some of the advantages of using chain couplings:
- Versatility: Chain couplings are available in a variety of sizes and styles to accommodate different applications.
- Reliability: Chain couplings are a reliable way to transmit power from 1 shaft to another.
- Cost-effectiveness: Chain couplings are a cost-effective way to transmit power from 1 shaft to another.
Here are some of the disadvantages of using chain couplings:
- Maintenance: Chain couplings require regular maintenance to ensure that they are operating properly.
- Noise: Chain couplings can be noisy, which can be a concern in some applications.
- Vibration: Chain couplings can vibrate, which can be a concern in some applications.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Simultaneous Handling of Axial Motion and Angular Misalignment by Beam Couplings
Beam couplings are designed to handle both axial motion and angular misalignment simultaneously in motion control systems. Their unique helical beam design allows them to accommodate various types of misalignment, providing flexibility in multiple axes. Let’s explore how beam couplings achieve this:
1. Axial Motion:
Beam couplings can compensate for axial motion, which occurs when the two connected shafts are not collinear and have some linear offset along their common axis. The helical beams of the coupling can elongate or compress to absorb the axial movement between the shafts. This axial flexibility enables the coupling to maintain a continuous and efficient connection even when the shafts experience slight linear displacement.
2. Angular Misalignment:
Angular misalignment refers to the situation where the two shafts are not perfectly aligned and are at an angle to each other. Beam couplings handle angular misalignment by allowing the helical beams to flex, bending at an angle to accommodate the misaligned shafts. The flexible beams can twist and adjust their shape as needed, providing a reliable connection between the shafts and transmitting torque efficiently.
3. Simultaneous Handling:
What makes beam couplings advantageous is their ability to handle both axial motion and angular misalignment simultaneously. As the shafts experience angular misalignment, the helical beams can flex to compensate for the misalignment angle. At the same time, if there is any axial motion between the shafts, the beams can elongate or compress to absorb the linear offset. This simultaneous handling of axial motion and angular misalignment allows beam couplings to maintain smooth operation and effective torque transmission even in applications with complex misalignment requirements.
It is essential to select the appropriate size and type of beam coupling based on the specific application’s misalignment characteristics and torque requirements. Properly installed and maintained beam couplings can provide reliable and efficient performance, ensuring accurate motion control and extended system life.
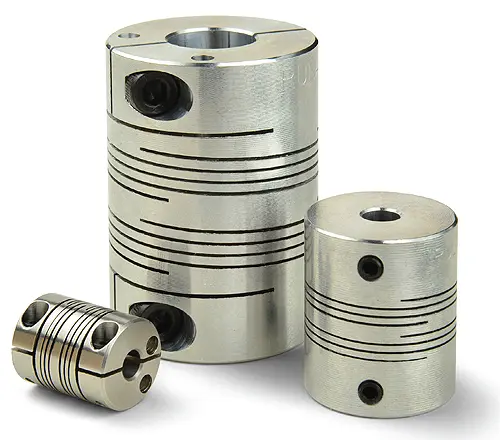

Real-World Examples of Successful Beam Coupling Installations and Their Benefits
Beam couplings have been widely adopted in various industries, and there are numerous real-world examples of successful installations showcasing their benefits. Here are some specific cases:
- Industrial Automation:
In a factory automation setting, beam couplings are used in robotic arms and automated machinery to transmit torque between motors and actuators. The flexibility of beam couplings helps compensate for minor misalignments, reducing wear on connected components and enhancing system reliability. Additionally, the low inertia of beam couplings enables faster response times, improving the overall efficiency of the automated systems.
- Medical Robotics:
Medical robots, such as surgical robots and diagnostic equipment, rely on precise and smooth motion control. Beam couplings, with their low backlash and high torsional stiffness, ensure accurate positioning and reduced vibration. The stainless-steel construction of some medical-grade beam couplings makes them suitable for sterilization processes, ensuring compliance with medical industry requirements.
- Photonic Systems:
In optical systems and laser equipment, beam couplings are used to connect stepper motors and motion stages. The damping properties of beam couplings help reduce vibrations, preventing optical misalignment and maintaining the stability of laser beams. This is critical for high-precision applications like laser cutting and micromachining.
- Satellite Components:
Beam couplings find applications in satellite components, where weight and size constraints are critical. Aluminum or lightweight alloys are used to minimize the overall mass while providing reliable power transmission between actuators and mechanisms. The low inertia of beam couplings contributes to smoother satellite movements and precise adjustments in space.
- Renewable Energy Systems:
Beam couplings are employed in renewable energy systems, such as solar tracking mechanisms and wind turbine pitch control systems. Their ability to handle harsh environmental conditions, such as wind and weather exposure, ensures consistent and efficient energy production. The use of non-magnetic materials in some couplings prevents interference with sensitive electronics.
The benefits of successful beam coupling installations in these real-world examples include:
- Improved Precision: Beam couplings provide accurate torque transmission, reducing positioning errors and enhancing the precision of motion control systems.
- Enhanced Reliability: The flexibility of beam couplings compensates for misalignments, reducing stress on connected components and extending the lifespan of the motion system.
- Reduced Vibrations: Beam couplings dampen vibrations, leading to smoother movements and preventing resonance-induced failures.
- Weight and Space Savings: In applications with weight and space constraints, beam couplings’ lightweight design is advantageous.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Beam couplings offer a cost-effective solution for motion control, especially when compared to more complex coupling options.
These successful installations demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of beam couplings across various industries, highlighting their ability to improve motion system performance, reliability, and efficiency.

Differences between Single-Beam and Multi-Beam Couplings
Single-beam and multi-beam couplings are two common types of beam couplings used in motion control applications. While they both provide flexibility for misalignment compensation, they have distinct differences in design and performance. Let’s explore these differences:
- Structure:
A single-beam coupling consists of a single helical beam that connects the two shafts. It is a straightforward design with a single helix providing angular misalignment compensation. On the other hand, a multi-beam coupling has multiple helical beams arranged in parallel around the circumference of the coupling. The multiple beams increase its flexibility and enable compensation for angular, axial, and parallel misalignment.
- Misalignment Compensation:
Both single-beam and multi-beam couplings are capable of compensating for misalignment between connected shafts. However, the level of compensation differs between the two types. Single-beam couplings are more suitable for applications with primarily angular misalignment. They can handle small amounts of axial and parallel misalignment but are less effective than multi-beam couplings in this regard. Multi-beam couplings, with their multiple beams, can efficiently accommodate more extensive misalignment in all three axes, making them suitable for applications with more complex misalignment requirements.
- Torsional Rigidity:
Single-beam couplings typically have lower torsional rigidity compared to multi-beam couplings. This means that single-beam couplings may exhibit slightly more torsional flexibility and compliance under torque compared to their multi-beam counterparts. As a result, multi-beam couplings are often preferred in applications where high torsional rigidity is essential to maintain precise motion control and minimize backlash.
- Applications:
The choice between single-beam and multi-beam couplings depends on the specific requirements of the application. Single-beam couplings are commonly used in applications where space is limited, and primarily angular misalignment needs to be compensated. They are suitable for less demanding misalignment scenarios and can be found in various motion control systems, including small automation machinery and robotics.
Multi-beam couplings are chosen for applications that require more comprehensive misalignment compensation. They excel in situations where misalignment can occur in multiple axes and are often used in precision motion control systems, optical equipment, and applications with high torsional rigidity and accuracy requirements.
In summary, single-beam and multi-beam couplings both offer flexibility for misalignment compensation in motion control systems. Single-beam couplings are simple, space-efficient, and suitable for applications with primarily angular misalignment. On the other hand, multi-beam couplings provide enhanced misalignment compensation in all three axes and offer higher torsional rigidity, making them ideal for precision applications with more complex misalignment requirements.


editor by CX 2024-04-08