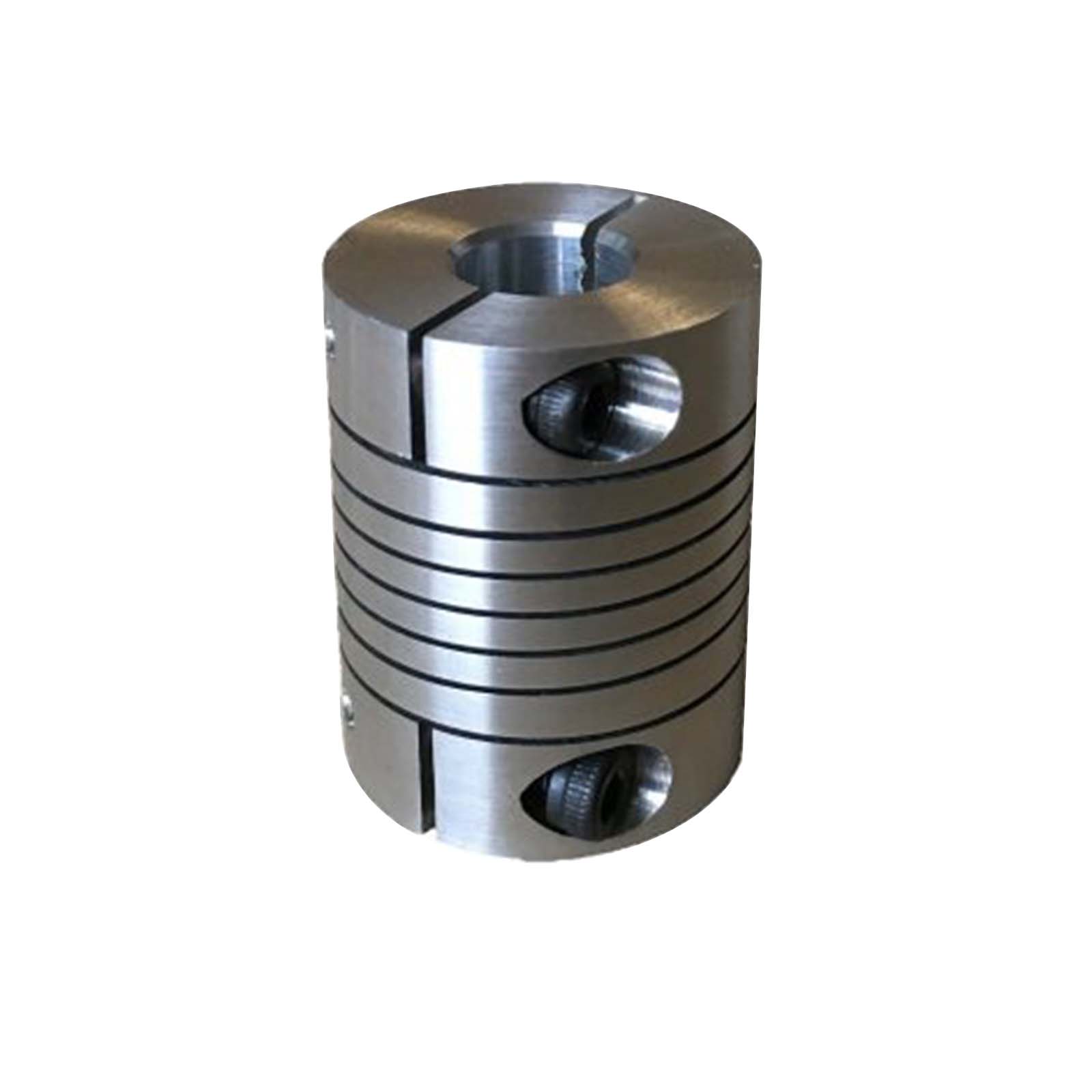
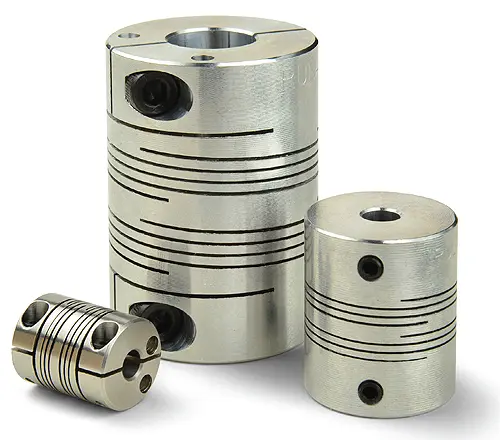
Product Description
| Product Name | Metal bellow coupling |
| Material | Aluminum |
| Type | BC16-82 |
| Structure | 1 shaft ( 1 / 1a / 1b ) with bore |
| Bore size | 4-42 mm |
| Weight | About 8-1200G g / pcs |
| packing | plastic bag +paper box +wooden box +wooden pallet |
1. Engineering: machine tools, foundry equipments, conveyors, compressors, painting systems, etc.
2. Pharmaceuticals& Food Processing: pulp mill blowers, conveyor in warehouse, agitators, grain, boiler, bakery machine, labeling machine, robots, etc.
3. Agriculture Industries: cultivator, rice winnower tractor, harvester, rice planter, farm equipment, etc.
4. Texitile Mills: looms, spinning, wrappers, high-speed auto looms, processing machine, twister, carding machine, ruler calendar machine, high speed winder, etc.
5. Printing Machinery: newspaper press, rotary machine, screen printer machine, linotype machine offset printer, etc.
6. Paper Industries: chipper roll grinder, cut off saw, edgers, flotation cell and chips saws, etc.
7. Building Construction Machinery: buffers, elevator floor polisher mixing machine, vibrator, hoists, crusher, etc.
8. Office Equipments: typewriter, plotters, camera, money drive, money sorting machine, data storage equipment, etc.
9. Glass and Plastic Industries: conveyor, carton sealers, grinders, creeper paper manufacturing machine, lintec backing, etc.
10. Home Appliances: vacuum cleaner, laundry machine, icecream machine, sewing machine, kitchen equipments, etc.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

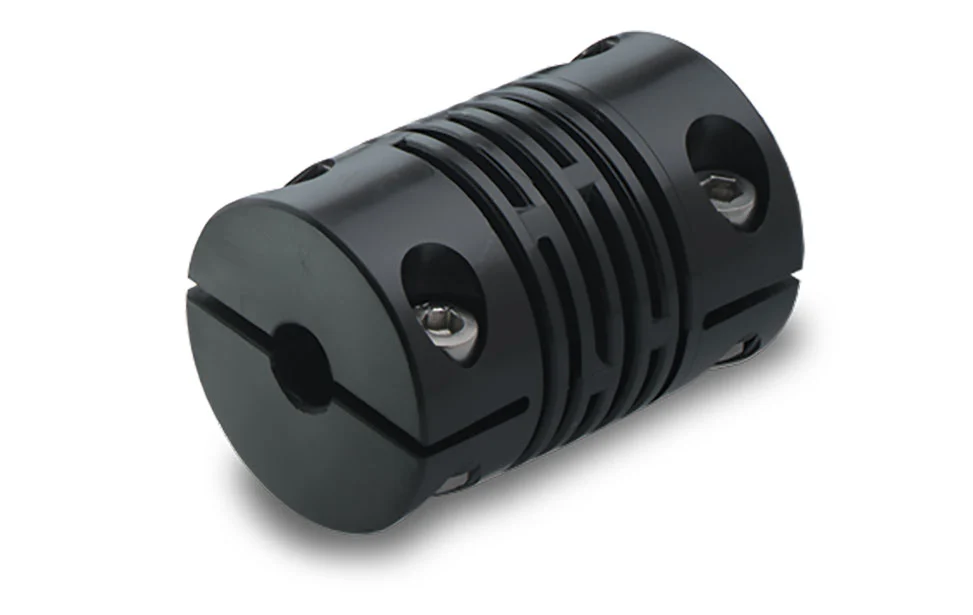
Temperature and Environmental Limits for Various Beam Coupling Materials
The temperature and environmental limits of beam coupling materials depend on their specific composition and properties. Different materials have varying degrees of resistance to temperature extremes, chemicals, humidity, and other environmental factors. Here are some common beam coupling materials and their associated temperature and environmental limits:
- 1. Stainless Steel:
Stainless steel beam couplings are known for their excellent mechanical properties and resistance to corrosion. They can typically operate within a wide temperature range, from -40°C to 300°C (-40°F to 572°F). Stainless steel is also resistant to most chemicals, making it suitable for various environments, including industrial and outdoor applications.
- 2. Aluminum:
Aluminum beam couplings offer lightweight construction and moderate mechanical properties. They have a more limited temperature range compared to stainless steel, typically operating between -20°C to 120°C (-4°F to 248°F). While aluminum has good corrosion resistance in certain environments, it is not as durable as stainless steel in harsh conditions.
- 3. Brass:
Brass beam couplings have reasonable mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. They are suitable for applications with temperatures ranging from -20°C to 100°C (-4°F to 212°F). Brass is more susceptible to corrosion in certain environments, so it is essential to consider the specific application’s conditions.
- 4. Plastic/Polymer:
Beam couplings made from plastic or polymer materials offer lightweight and cost-effective solutions. However, their temperature limits are more restricted compared to metal couplings. They typically operate between -30°C to 80°C (-22°F to 176°F). These couplings may not be suitable for high-temperature or chemically aggressive environments.
- 5. Carbon Steel:
Carbon steel beam couplings are known for their strength and mechanical properties. They generally operate between -40°C to 120°C (-40°F to 248°F). Carbon steel is vulnerable to corrosion, so it may not be ideal for applications in corrosive or humid environments without proper protection.
It’s crucial to consider the temperature and environmental conditions of your specific application when selecting a beam coupling material. Choosing a material that can withstand the intended operating conditions will ensure the longevity and reliable performance of the coupling.
Additionally, keep in mind that various beam coupling manufacturers may offer specific variations of materials with different properties and limits. Always refer to the manufacturer’s datasheets and technical documentation for precise information on the temperature and environmental limits of their beam coupling products.

Safety Considerations for Installing or Using Beam Couplings in Industrial Setups
When installing or using beam couplings in industrial setups, several safety considerations should be taken into account to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the motion control systems. Here are some important safety considerations:
- Proper Installation:
Ensure that beam couplings are correctly installed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Follow the recommended torque values for tightening set screws or clamps to avoid over-tightening or under-tightening, which could lead to coupling failure or excessive wear.
- Shaft Alignment:
Accurate shaft alignment is crucial to prevent unnecessary stress on the coupling and connected components. Misalignment can lead to premature wear, vibrations, and reduced system performance. Utilize alignment tools and techniques to achieve precise shaft alignment within the coupling’s specified tolerances.
- Overloading:
Avoid exceeding the beam coupling’s rated torque capacity or maximum axial load. Overloading the coupling can lead to deformation, coupling failure, or damage to connected equipment. Ensure that the coupling is appropriately sized for the application’s torque requirements.
- Regular Inspection:
Perform routine inspections of beam couplings to check for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Address any issues promptly and replace worn or damaged couplings to prevent unexpected failures.
- Environmental Conditions:
Consider the operating environment when selecting beam couplings. Different materials offer varying levels of resistance to corrosion, temperature extremes, and other environmental factors. Choose a material that can withstand the specific conditions of the industrial setup.
- Protective Enclosures:
If the beam couplings are exposed to moving parts or hazardous equipment, consider using protective enclosures or guards to prevent accidental contact and ensure operator safety.
- Regular Maintenance:
Follow a regular maintenance schedule for the entire motion control system, including beam couplings. Lubricate moving parts as recommended by the manufacturer and replace worn components to maintain reliable operation.
- Training and Awareness:
Ensure that personnel involved in the installation, operation, and maintenance of the motion control system are properly trained and aware of safety procedures. Emphasize the importance of following safety guidelines to prevent accidents and injuries.
By taking these safety considerations into account, industrial setups can enhance the safety and efficiency of their motion control systems. Regular maintenance, proper installation, and adherence to safety guidelines are essential to ensuring the longevity and reliable performance of beam couplings and the overall safety of the workplace.

Handling Misalignment and Compensating for Shaft Offset in Beam Couplings
Beam couplings are designed to handle misalignment between connected shafts and compensate for shaft offset in motion control systems. Their flexible and helical beam structure allows them to accommodate various types of misalignment, ensuring smooth and reliable operation. Here’s how beam couplings handle misalignment and compensate for shaft offset:
- Helical Beam Design:
Beam couplings consist of one or more helical beams, which are thin, flexible metal strips arranged in a helix shape. The helical beam design gives beam couplings their characteristic flexibility, allowing them to bend and twist in response to misalignment and shaft offset.
- Angular Misalignment:
If the connected shafts are not collinear and are at an angle to each other, it results in angular misalignment. Beam couplings can handle angular misalignment by allowing the helical beams to flex, bending at an angle to accommodate the misaligned shafts. The flexibility of the beams enables the coupling to transmit torque smoothly even when the shafts are not perfectly aligned.
- Axial Misalignment:
Axial misalignment occurs when the two shafts are not on the same axis or are not aligned in the same line. Beam couplings can compensate for axial misalignment by permitting the helical beams to elongate or compress in the axial direction. This axial flexibility allows the coupling to accommodate the offset between the shafts without causing excessive stress on the components.
- Parallel Misalignment:
Parallel misalignment refers to the situation where the two shafts are not at the same height or parallel to each other. Beam couplings handle parallel misalignment by permitting the helical beams to shift laterally. This lateral movement allows the coupling to adjust to the offset between the shafts and maintain an effective connection.
- Compensation Range:
Beam couplings have a specified range of misalignment they can accommodate. The amount of misalignment they can handle depends on the number of helical beams and the design of the coupling. Multi-beam couplings typically have a higher misalignment compensation range compared to single-beam couplings, making them more suitable for applications with more significant misalignment requirements.
- Limitations:
While beam couplings can compensate for a certain degree of misalignment, they do have limitations. Excessive misalignment beyond the coupling’s rated capacity can lead to premature wear, increased stress on the components, and reduced coupling performance. It’s essential to operate the beam coupling within its specified misalignment limits to ensure optimal functioning and longevity.
In summary, beam couplings handle misalignment and compensate for shaft offset by virtue of their flexible helical beam design. The ability to bend, twist, elongate, and shift laterally enables them to accommodate angular, axial, and parallel misalignment in motion control systems. Choosing the appropriate beam coupling type and staying within its rated misalignment range are essential to ensure effective compensation and reliable operation in various applications.


editor by CX 2024-04-25