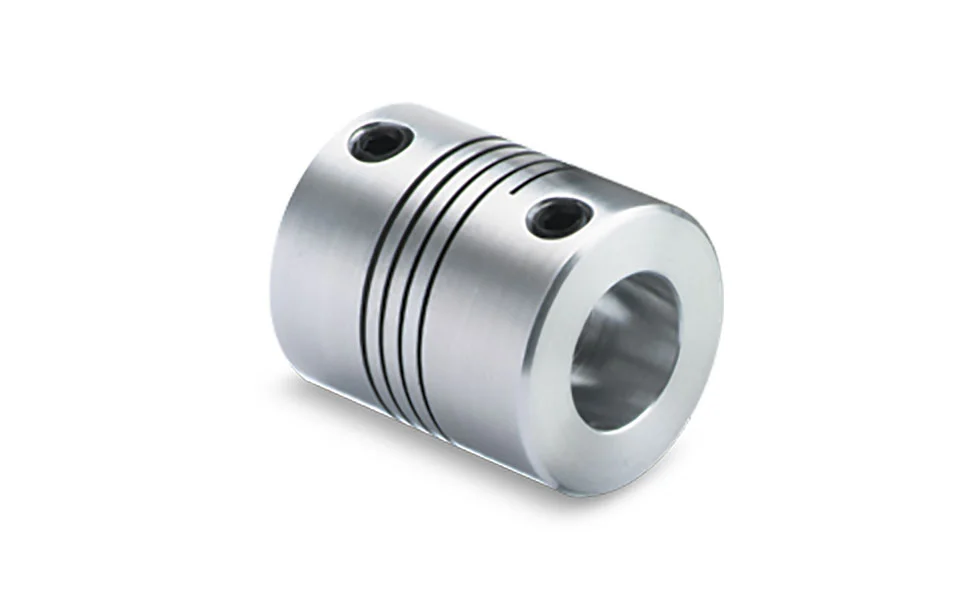
Product Description
| Product Name | Flexible beam coupling |
| Material | Aluminum |
| Type | FC16-63 |
| Structure | 1 shaft ( 1 / 1a / 1b ) with bore |
| Bore size | 5-35 mm |
| Weight | About 9.2-580G g / pcs |
| packing | plastic bag +paper box +wooden box +wooden pallet |
1. Engineering: machine tools, foundry equipments, conveyors, compressors, painting systems, etc.
2. Pharmaceuticals& Food Processing: pulp mill blowers, conveyor in warehouse, agitators, grain, boiler, bakery machine, labeling machine, robots, etc.
3. Agriculture Industries: cultivator, rice winnower tractor, harvester, rice planter, farm equipment, etc.
4. Texitile Mills: looms, spinning, wrappers, high-speed auto looms, processing machine, twister, carding machine, ruler calendar machine, high speed winder, etc.
5. Printing Machinery: newspaper press, rotary machine, screen printer machine, linotype machine offset printer, etc.
6. Paper Industries: chipper roll grinder, cut off saw, edgers, flotation cell and chips saws, etc.
7. Building Construction Machinery: buffers, elevator floor polisher mixing machine, vibrator, hoists, crusher, etc.
8. Office Equipments: typewriter, plotters, camera, money drive, money sorting machine, data storage equipment, etc.
9. Glass and Plastic Industries: conveyor, carton sealers, grinders, creeper paper manufacturing machine, lintec backing, etc.
10. Home Appliances: vacuum cleaner, laundry machine, icecream machine, sewing machine, kitchen equipments, etc.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Comparison of Beam Couplings to Other Coupling Types in Terms of Backlash and Torsional Stiffness
When considering coupling options for motion control systems, two critical performance characteristics to evaluate are backlash and torsional stiffness. Backlash refers to the amount of rotational play or free movement between the connected shafts, while torsional stiffness indicates a coupling’s ability to resist torsional deformation when transmitting torque. Let’s compare beam couplings to other common coupling types in terms of these factors:
- Beam Couplings:
Beam couplings generally exhibit low to minimal backlash due to their single or multiple helical beam design. The helical beams provide some flexibility to accommodate misalignment, but they maintain a relatively tight connection between the shafts, resulting in low backlash. This characteristic is especially valuable in precision motion control applications where eliminating play is essential for accurate positioning.
In terms of torsional stiffness, beam couplings offer moderate to high values. The helical beams provide good torsional rigidity, making them suitable for applications that demand precise torque transmission and minimal torsional deflection. However, compared to other types like disc or jaw couplings, beam couplings may have slightly lower torsional stiffness.
- Disc Couplings:
Disc couplings are known for their excellent torsional stiffness, providing robust torque transmission and minimal torsional deformation. They are ideal for applications requiring high precision and where torsional rigidity is critical.
Regarding backlash, disc couplings typically have low to negligible values. Their design allows for precise and direct transmission of torque between the shafts, resulting in minimal rotational play.
- Jaw Couplings:
Jaw couplings offer low to moderate torsional stiffness, making them suitable for applications with moderate torque requirements. They provide some flexibility to handle misalignment, but their torsional rigidity is not as high as disc couplings or certain types of beam couplings.
Backlash in jaw couplings can vary depending on the specific design and materials. Some jaw couplings may have slightly more backlash compared to beam or disc couplings due to the elastomeric spider element used in their construction.
- Oldham Couplings:
Oldham couplings offer low backlash performance due to their unique three-piece design, which incorporates two outer hubs and a middle disk. The design allows for consistent torque transmission and minimal play between the shafts.
Torsional stiffness in Oldham couplings is moderate, providing a balance between flexibility and rigidity. While not as rigid as disc couplings, they still offer reliable torque transmission for various motion control applications.
In summary, beam couplings offer low to minimal backlash and moderate to high torsional stiffness, making them suitable for precision motion control applications that require a balance between flexibility and rigidity. Disc couplings provide excellent torsional stiffness and low backlash, making them an ideal choice for high-precision applications. Jaw couplings and Oldham couplings offer moderate performance in both backlash and torsional stiffness and are well-suited for applications with moderate torque and misalignment compensation requirements.
When selecting a coupling type, consider the specific needs of your application, such as the required precision, torque capacity, and misalignment compensation. Each coupling type has its advantages and limitations, and choosing the right one will contribute to the overall performance and reliability of your motion control system.

Materials Used in Manufacturing Beam Couplings
Beam couplings are commonly made from various materials, each offering unique properties that suit different application requirements. Some of the most common materials used in manufacturing beam couplings include:
- Aluminum:
Aluminum is a lightweight and cost-effective material commonly used in beam coupling construction. Aluminum beam couplings are ideal for applications where weight reduction is essential, such as in robotics or aerospace systems. They provide moderate mechanical strength and flexibility while offering good resistance to corrosion.
- Stainless Steel:
Stainless steel is a popular choice for beam couplings due to its excellent mechanical properties and high corrosion resistance. Stainless steel couplings are well-suited for demanding applications that require strength, durability, and resistance to harsh environments. They are commonly used in industries such as food processing, medical equipment, and marine applications.
- Brass:
Brass is a material known for its good electrical conductivity and moderate strength. Brass beam couplings are suitable for specific applications that require electrical grounding or where non-magnetic properties are essential. However, compared to stainless steel or aluminum, brass couplings may have slightly lower mechanical strength and corrosion resistance.
- Plastic/Polymer:
Plastic or polymer beam couplings are chosen for their lightweight and cost-effective nature. They are often used in applications where weight reduction is critical, and they offer electrical insulation properties. However, plastic couplings may have lower mechanical strength compared to metal couplings and are not suitable for high-torque applications or extreme environmental conditions.
- Carbon Steel:
Carbon steel is a robust and widely used material for beam couplings. Carbon steel couplings offer good mechanical strength and are suitable for various industrial applications. However, they may not provide the same level of corrosion resistance as stainless steel and may require proper maintenance to prevent rusting.
The choice of material depends on the specific needs of the application, including factors such as required strength, weight constraints, environmental conditions, and corrosion resistance. Manufacturers often provide a range of material options for their beam couplings to accommodate diverse industrial and commercial uses.

Different Types of Beam Couplings for Various Applications
Beam couplings come in various designs to meet different application requirements. Each type offers specific advantages and limitations. Here are some common types of beam couplings used in various applications:
- 1. Single-Beam Couplings:
Single-beam couplings consist of a single helical beam that connects the two shafts. They are simple in design and provide good flexibility for compensating angular misalignment. These couplings are ideal for applications where space is limited, and angular misalignment is the primary concern.
- 2. Multi-Beam Couplings:
Multi-beam couplings have multiple helical beams arranged in parallel around the circumference of the coupling. This design enhances the coupling’s flexibility and allows for better compensation of angular, axial, and parallel misalignment. Multi-beam couplings are commonly used in applications requiring more comprehensive misalignment compensation and smoother torque transmission.
- 3. Bellows Couplings:
Bellows couplings use a thin-walled, accordion-like metal bellows as the flexible element. This design provides high flexibility, making them suitable for applications with significant angular and axial misalignment. Bellows couplings are also effective at damping vibrations and providing precise motion control in sensitive systems.
- 4. Servo Disc Couplings:
Servo disc couplings consist of a series of thin metal discs stacked together with a central spacer. This design allows for high torsional rigidity and excellent misalignment compensation. Servo disc couplings are often used in precision applications where minimal backlash and high torque transmission are required.
- 5. Slit Couplings:
Slit couplings have one or more slits cut into the helical beam, providing additional flexibility. The slits allow for better compensation of misalignment and increased torsional flexibility. Slit couplings are commonly used in applications with moderate misalignment requirements and where vibration dampening is essential.
- 6. Step Beam Couplings:
Step beam couplings have helical beams with varying thickness along their length. This design provides a progressive flexibility gradient, allowing for smoother torque transmission and better misalignment compensation. Step beam couplings are often used in applications where shock absorption and vibration isolation are crucial.
- 7. Jaw Couplings with Beam Elements:
Jaw couplings with beam elements combine the features of traditional jaw couplings with the flexibility of beam couplings. They offer excellent misalignment compensation, shock absorption, and easy installation, making them suitable for various power transmission and motion control applications.
The choice of the most suitable beam coupling type depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as the level of misalignment, torque capacity, damping requirements, and the overall system design. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each type will help in selecting the best beam coupling for a particular application, ensuring efficient and reliable performance in various mechanical systems.


editor by CX 2024-02-13